What is Proof of Reserve Audit?
Proof of reserves audit (POR) is a type of audit that verifies that a cryptocurrency exchange or other financial institution has the cryptocurrency assets it claims to have on hand. The purpose of a proof of reserves audit is to provide transparency and assurance to customers and regulators that the company is financially sound and able to meet its obligations.
There are a number of cryptocurrency exchanges that use proof of reserves audits to demonstrate their financial stability and transparency. Some examples of exchanges that have undergone proof of reserves audits include Coinbase, Bitfinex, and Kraken.
How is a proof of reserves audit performed?
To perform a proof of reserves audit, an independent third party (such as an accounting firm or audit firm) will review the company’s financial records and conduct various tests to verify that the company has the cryptocurrency assets it claims to have on hand. This may involve reviewing the company’s cryptocurrency wallets and transactions, as well as reconciling the company’s assets and liabilities. The audit firm may also request additional documentation or conduct on-site inspections to confirm the company’s financial position.
Benefits of PoR audits
One of the main benefits of proof of reserves audits is that they provide transparency and reassurance to customers and regulators that a company is financially stable and able to meet its obligations. This can help to build trust and confidence in the company, as well as enhance its reputation.
Additionally, proof of reserves audits can help to prevent fraud and mismanagement by ensuring that companies are accurately reporting their assets and liabilities. This can help to protect customers’ funds and assets and prevent financial losses.
Another advantage worth mentioning is that PoR is also an appealing prospect for regulators as this self-regulating measure is in line with their overarching vision for the industry. In essence,
Proof of Reserves is a win-win situation for all parties involved: the users, the industry, and the government.
Merkle Tree
A Merkle tree, also known as a hash tree, is a data structure used in cryptocurrency to efficiently verify large sets of data. It is named after Ralph Merkle, who invented the concept in 1979.
One concept that is often used in proof of reserves audits is the “merkle tree.” A merkle tree is a data structure that allows for the efficient verification of large sets of data. In the context of a proof of reserves audit, a merkle tree may be used to efficiently verify that a company has the cryptocurrency assets it claims to have on hand.
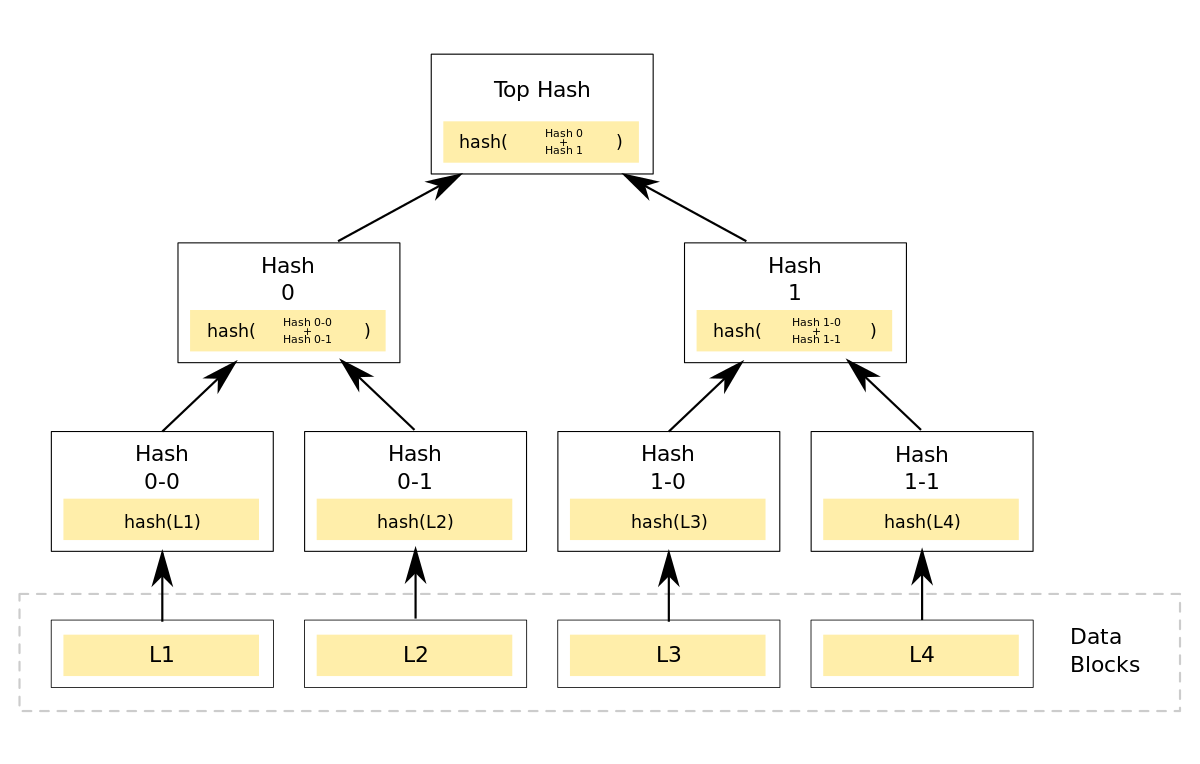
To use a merkle tree in a proof of reserves audit, the audit firm would create a list of all the company’s cryptocurrency assets and transactions. This list would be hashed (a cryptographic function that takes an input and produces a fixed-size output) and organized into a tree-like structure, with each “leaf” node representing a hash of a single transaction or asset. The hashes of each leaf node are then combined and hashed again to create the next level of the tree, and this process continues until a single “root” hash is produced.
The root hash can then be used to efficiently verify that the company has the cryptocurrency assets it claims to have on hand. If the company’s records match the root hash, it can be assumed that the company has the assets it claims to have.
Conclusion
Overall, proof of reserves audits are an important tool for ensuring the financial stability and transparency of cryptocurrency exchanges and other financial institutions. They provide reassurance to customers and regulators that a company is able to meet its obligations and help to prevent fraud and mismanagement. The use of a merkle tree in a proof of reserves audit can help to efficiently verify large sets of data and ensure the accuracy of the audit.

